Physics
| Eng | 繁中 | 日本語 | 한국어 | 简中 |
Tweaking Physics
System-wide physics settings
You can locate the system-wide physics settings in Settings -> Options -> Physics.
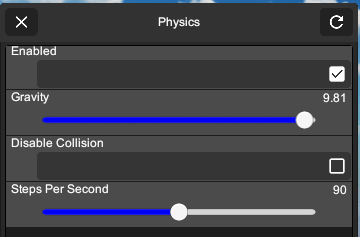
- Enabled
- Turn physics simulation on and off
- Gravity
- Change gravity force. Set it to negative will reverse the gravity direction.
- Disable Collision
- Controls collision between model parts. There are 2 types of colliders in a model, type A are the ones that move with animation, like arms and legs, type B are the ones that move freely, usually they are connected to other parts by one or more joints. By default type B will collide with type A but if you turn “Disable Collision” on, then type B objects will no longer collide with type A objects and will penetrate through.
- Steps per second
- Physics simulation are calculated with a certain interval between steps, and it works best if it is a fixed interval. This option controls how many simulation is performed within a second. The more the better but too many steps will slow down your FPS. It’s best to match it with your FPS for smooth animation.
PMX Model specific settings
You can locate the model specific physics settings in model settings -> Options -> Physics
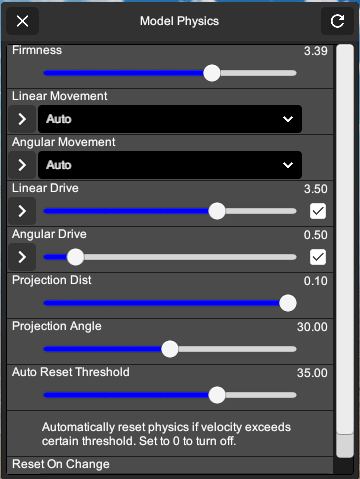
- Firmness
- This is an overall multiplier applied to the spring force of all joints. Increasing the value will reduce movements. On top of this you can control spring forces for linear and angular movements individually using the settings below.
- Linear Movement
- Choose how linear movements are restricted for all joints. Auto will set restriction based on the linear limit defined in the model. If the limit is smaller than a small amount, it will be locked otherwise it will be limited. “Bounciness” controls how much velocity is preserved when it hit the edge of its limit and bounce back. “Contact distance” decides when to apply limit spring force when it goes near its limit, 0 means it moves freely until it actually hits the limit, 1 means that the force is always applied when it is with in the limit.
- Angular Movement
- Similar to the linear movement above, this one controls angular movements of all joints.
- Linear Drive
- This controls how much spring force is used to make the connected object to return to its original positoin. The “Target” setting here controls where the neutural position is.
- Angular Drive
- This controls the force that make objects to return to their orientation.
- Projection Dist
- Projection distance. If the distance between the 2 connected objects is greater than the value defined here, the objects will be moved back to avoid runaway situation.
- Projection Angle
- Similar to above, this one controls rotation.
- Reset on change
- Once toggled, whenever a change is made here, all the bones are reset to their initial position before the new settings values are applied. This can prevent bones drifting off while changing physics settings. But sometimes this makes it hard to observe the effect of the change, in that case you can turn this option off before you make your changes, and then turn it back on after you found your ideal settings.
Within movement and drive settings, there are a few common setting values
- Spring Force
- Used to calculate force based on Hooke’s law
- Damp / drag
- How much force is applied to stop the movements in ralation to the current velocity.
XPS Model Specific Settings
XPS models don’t come with physics definitions so the program does not know where to add physics components. To deal with this several physics settings are added to each XPS model for you to configure physics components on a XPS model.
Bone Colliders
This setting creates colliders on common body parts to allow them to interact with other physics objects. Use the slider to change the size to fit the model body build.
Boobs Physics
Eventhough this is turned on by default it does nothing until you select the correct boobs related bones from the settings. Usually they are child bones of torso2 and have 2 of them one for each side.
- Spring, Mass, Damp
- controls physics properties of the joints.
- Limit
- controls how much rotation they can move from their parent bones
- Counter Gravity
- lifts the boobs up by the selected degrees to counter the effect of gravity pulling them down.
- Collider Radius
- controls size of the collider, better to set it to a value that matches the model.
- Anchor and Center
- controls the position of the joints.
Hair Physics
Similar to the boobs settings, you need to select bones for it to work. Usually they are child bones of head. Sometime it takes a bit digging to find the right bones. The way it creates physics componenets is that from the bones you selected, it will connect all the child bones and their children until the end is reached to form a tree structure of joints and colliders.
- Collider Radius
- The colliders are cylinder shaped and the collider radius controls the diameter.
- Skip First X Bones
- This will tell the program to skip the first x number of bones when creating the “tree”, effectively allows you to avoid having to select each bones when there are too many.
Cloth Physics
This is similar to hair physics but it also has horizontal connection between the branches of the “tree”, forming a “mesh”